Call for Abstract
Scientific Program
21st World Congress on Pharmaceutical Sciences and Innovations in Pharma Industry, will be organized around the theme “New Challenges in Pharma Industries and Growth of Pharmaceutical Research”
Pharmaceutical Sciences 2021 is comprised of 18 tracks and 50 sessions designed to offer comprehensive sessions that address current issues in Pharmaceutical Sciences 2021.
Submit your abstract to any of the mentioned tracks. All related abstracts are accepted.
Register now for the conference by choosing an appropriate package suitable to you.
Medico-Marketing focusses on exchange of drug information among drug manufacturing company and the recommending doctor, Nurse, Pharmacist or with the end user. The intention behind this data exchange is to describe the Pharmaceutical Company’s products and how it will benefit the patient community in diagnosis or management of the human ailments.

- Track 1-1close collaboration between medical and marketing team.
- Track 1-2Promotion of a pharmaceutical product must be consistent with the terms of the product authorization.
A platform aimed to connect Entrepreneurs, Proposers and the Investors worldwide. It's intended to create and facilitate the most optimized and viable meeting place for engaging people in global business discussions, evaluation and execution of promising business ideas. An investor could be able to find out the highest potential investment opportunities globally, which provide good return on investment.

- Track 2-1Innovations in Formulations Research.
Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology deals with emerging new technologies for developing customized solutions for drug delivery systems. The drug delivery system positively impacts the rate of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of the drug or other related chemical substances in the body. In addition to this the drug delivery system also allows the drug to bind to its target receptor and influence that receptor’s signalling and activity. Pharmaceutical nanotechnology embraces applications of nanoscience to pharmacy as nanomaterials, and as devices like drug delivery, diagnostic, imaging and biosensor.

- Track 3-1Rationale for polymer conjugation.
- Track 3-2Enhanced solubility and dissolution.
- Track 3-3Polymer-drug conjugates.
The pharmaceutical sciences combine broad range of scientific disciplines that are critical to the discovery and development of new drugs and therapies. Pharmaceutical Sciences is a dynamic and interdisciplinary field that aims to integrate fundamental principles of physical and organic chemistry, engineering, biochemistry, and biology to understand how to optimize delivery of drugs to the body and translate this integrated understanding into new and improved therapies against human disease. At the many of institutes internationally recognized faculty contribute to the field through inquiry into the underlying mechanisms of drug interactions with the human body and development of advanced synthetic or biologically-derived materials that can modulate these interactions in pursuit of better and safer therapies and drug products.

- Track 4-1combine broad range of scientific disciplines that are critical to the discovery and development of new drugs and therapies.
- Track 4-2Underlying mechanisms of drug interactions .
Drug absorption is set by the drug’s chemistry properties, formulation, and route of administration. Dosage forms (e.g. tablets, capsules, solutions), consisting of the drug and alternative ingredients, square measure developed to lean by numerous routes (e.g. oral, buccal, sublingual, rectal, parenteral, topical, inhalational). In spite of the route of administration, medicine should be in answer to be absorbed.
- Track 5-1 Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics combines the skills of an interdisciplinary team of clinicians pharmacists and nurses.
- Track 5-2 understanding of disease processes evidence-based clinical pharmacology and optimal drug regimes.
- Track 5-3Many new and revised illustrations.
- Track 5-4Dosage reference sources given where appropriate, along with useful websites and further reading for each chapter.
Big pharmaceutical companies develop new business models to cope with the innovation crisis (patent loss, drying up of pipelines) and to improve their productivity in R&D and innovation. These pressures led big players to transform or reinvent their business models to sustain value creation from R&D and innovation. However, to our knowledge, there is still a lack of understanding regarding the “strategic alignment” of these organizational changes and on how they are perceived by organizational members.

- Track 6-1new drug development
- Track 6-2science and technology are transforming healthcare, improving the probability of success in R&D
Some of the people believes that digital capabilities are not only critical to Pharmaceutical companies’ ability to improve the way they roll out new products, but to increasing the Pharmaceutical industry’s contribution to health care by enabling it to provide innovative services to improve patients’ outcomes. In order to increase the perceived value of Pharma within the health care system, the industry is striving to respond to the needs of all stakeholders: health care professionals, patients and payer’s. In the meantime, the culture of Pharmaceutical companies is shifting from one of separate departments working vertically to one that is cross functional .

- Track 7-1Pharmaceutical companies can play a central role in the digital revolution of healthcare.
- Track 7-2empowering healthcare professionals with credible information.
- Track 7-3Innovation& challenges.
The downturn in the global economy has forced Pharmaceutical and life sciences companies to focus on cost-saving initiatives, putting stress on finance departments. Although optimizing costs will always be important, reinvigorating R&D will most likely be a top strategic initiative for these companies as well. Most big Pharmaceutical companies are under competitive pressure from generic drug makers pressure that will become more intense as an increasing number of patents for “blockbuster” drugs expire during the next few years.

- Track 8-1investments in R&D to increase revenue generation from the biotech sector.
- Track 8-2They should adapt and review their strategies.
Yet over the past decade in particular, most of the Big Pharma’s have adopted small molecule generics in one shape or form into their overall business model. And many of them openly talk about the “innovation headroom” that a healthy low-priced generics market enables i.e. the money saved on off-patent drugs can be used to fund high-priced new innovations. They have recognized that they cannot fight the realities of aging populations and healthcare economics .
- Track 9-1Health care economics.
- Track 9-2Innovation head room.
Globalized Pharma Sector is based on gaining information on changing structure of competition and increased competitiveness, lack of brand new products, despite increased investments into R&D (Research& Development) activities, increased importance of regulatory issues (registrations, intellectual property rights, litigations), fast consolidation and concentration of the world Pharmaceutical industry can be known as the Globalized Pharma Sector.

- Track 10-1Shares of global pharmaceutical markets.
- Track 10-2Global market presence.
- Track 10-3Provides both opportunities and risks.
The area unit variety of motives for extending the merchandise development outside of the mature, developed economies (e.g. the EU and therefore the US) and most of them have faith in the high population and market potential of rising markets. FDA guidance for clinical investigations and Pharmaceutical development goes a lot of and a lot of international within the direction of rising markets that tend to supply solutions for the patient achievement and overall development prices and timelines.
- Track 11-1Involves both legal and health experts.
- Track 11-2TRIPS agreement.
Pharmaceutical Process Validation is the most important and recognized parameters of CGMPs. Quality cannot be adequately assured by in-process and finished inspections and testing but it should be built in to the manufacturing process. These processes should be controlled in order that the finished product meets all quality specifications. Validation is one of the important steps in achieving and maintaining the quality of the final product. The requirement of process validation appears of the quality system (QS) regulation. The goal of a quality system is to consistently produce products that are fit for their intended use.
- Track 12-1Checking of installation of equipment, piping, services and instrumentation.
- Track 12-2Verification of materials of construction.
Supply chain management (SCM) is the integration of key business processes across the supply chain for the purpose of creating value for customers and stakeholders. Indeed, supply chain management integrates supply and demand within and across companies in an efficient business model. The Council of Supply Chain Management Professionals defines supply chain management as planning and management of all activities involved in sourcing, procurement, conversion and all logistics activities. There are various aspects of optimizing in the supply chain; eliminating bottlenecks, balancing between lowest material cost and transportation, optimizing manufacturing flow, maintaining the right mix and location of factories and warehouses, vehicle routing analysis, dynamic programming and efficient use of capacities, inventories, and labours are of main aspects of supply chain optimization.
- Track 13-1Major research theme in process operations.
- Track 13-2directly addresses the issues faced in the pharmaceutical sector.
- Track 13-3Pipeline management.
Good Manufacturing Practices quality of drugs is essentially the responsibility of manufacturers. GMP Guidelines are means to assure this very quality of drugs. CGMP refers to the Current Good Manufacturing Practice regulations enforced by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). CGMPs provide for systems that assure proper design, monitoring, and control of manufacturing processes and facilities. Adherence to the CGMP regulations assures the identity, strength, quality, and purity of drug products by requiring that manufacturers of medications adequately control manufacturing operations. GMP is actually good common sense quality management quality assurance GMP production and quality control.

- Track 14-1Quality Assurance.
- Track 14-2Clear, written instructions and procedures.
- Track 14-3Annual Product Quality Review.
- Track 14-4Basic requirements for GMP.
- Track 14-5AIM OF Good Manufacturing Practices.
Packaging plays an important role in providing protection, presentation, convenience, identification information, and compliance of a product during storage, transportation, display and until the product is safely consumed. Packaging may be considered as a system by which the product safely reaches from producer to consumer. The track mainly focuses on recent advances in packaging technology and packaging material. Many types of symbols for package labelling should be nationally and internationally standardized. Packaging symbols represent product certifications, trademarks, proof of purchase .
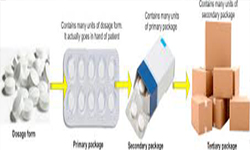
- Track 15-1Blow- fill- seal technology was initially used for filling many categories of liquids, such as non-sterile devices, foods and cosmetics. Recently, Blow- fill- seal technology is used to produce aseptically sterile pharmaceuticals such as respiratory solut
- Track 15-2Novel Laser Coding Technology for Pharmaceutical Glass Containers Glass syringes can now be individually coded / safe process free of micro-cracks / Reliable Track & Trace. A completely new laser-coding system enables glass containers for parenteral use t
- Track 15-3Induction Cup sealing technology is used to create airtight and hermetic seals on the neck of the container. The process of Induction cup sealing is based on the principle that a conductive material like aluminum foil heats up on exposure to high frequen
Pharmaceutical engineering deals with Pharmaceutical Science and technology that involves development and manufacturing of products, processes, and components in the Pharmaceuticals industry (i.e. drugs & biologics). While developing Pharmaceutical products involves many interrelated disciplines (e.g. medicinal chemists, analytical chemists, clinicians/pharmacologists, pharmacists, chemical engineers, biomedical engineers, etc.), the specific subfield of "Pharmaceutical engineering" has only emerged recently as a distinct engineering discipline.

- Track 16-1Analytical and quality control processes.
- Track 16-2Continuous real-time quality is ensured.
- Track 16-3Risk-based regulatory approaches recognize the level of scientific understanding of how formulation and manufacturing process.
Drug development focusses on launch of new Pharmaceutical drug to the market once a lead compound has been identified through the process of drug discovery. It includes pre-clinical research on microorganisms and animals, filing for regulatory status, such as via the United States Food and Drug Administration for an investigational new drug to initiate clinical trials on humans, and may include the step of obtaining regulatory approval with a new drug application to market the drug.
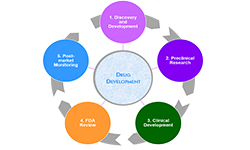
- Track 17-1Drug development is a lengthy, complex, and costly process
- Track 17-2 Target identification challenging.
- Track 17-3Increased clinical phenotyping and endotyping.
In the fields of medicine, biotechnology and Pharmacology, drug discovery is the process by which new candidate medications are discovered. Modern drug discovery involves the identification of screening hits, medicinal chemistry and optimization of those hits to increase the affinity, selectivity (to reduce the potential of side effects), efficacy or potency, metabolic stability (to increase the half-life), and oral bioavailability.

- Track 18-1Target identification and Validation
- Track 18-2Hit identification and Validation
- Track 18-3 Moving from a hit to a lead
- Track 18-4Lead Optimization
- Track 18-5Late Lead Optimization
